Introduction
Working with SQL databases in Node.js doesn't have to feel like writing a PhD thesis in raw SQL. In this guide, you'll learn how to build a simple but real-world Todo List App using modern tools: TypeScript, Drizzle ORM, and Neon DB.
Whether you're a beginner or looking to level up your backend workflow, this article will help you set up a type-safe, scalable, and serverless-ready SQL database using PostgreSQL without the usual headache.
What Is a Relational vs Non-Relational Database?
Before we dive into the tools, let's clarify two core types of databases:
Relational Database
A relational database organizes data into tables (rows and columns). These tables can be connected (or related) using keys like user_id. It's ideal when data consistency and structure are important.
Example (PostgreSQL Schema):
CREATE TABLE todos (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
task TEXT NOT NULL,
completed BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE
);
Non-Relational Database
A non-relational database (often called NoSQL) stores data in formats like documents (JSON), key-value pairs, or graphs. It's more flexible and scalable for unstructured or fast-changing data.
Example (MongoDB Document):
{
"_id": "1",
"task": "Buy milk",
"completed": false
}
🛠️ What Is an ORM?
ORM stands for Object-Relational Mapping. It's a tool that lets you write database queries using your application's language (like TypeScript), instead of raw SQL.
It helps with:
- Type safety
- Cleaner, more maintainable code
- Fewer bugs and less boilerplate
Without ORM:
INSERT INTO todos (task, user_id) VALUES ('Buy milk', 1);
With ORM (Drizzle):
await db.insert(todos).values({ task: "Buy milk", userId: 1 });
Meet Drizzle ORM
Drizzle ORM is a TypeScript-first ORM with:
- Strong typing
- Lightweight and fast
- Serverless-ready
- Familiar SQL-like syntax
As their docs put it, it's a "headless TypeScript ORM with a head" — meaning it gives you control without losing flexibility or dev experience.
What Is Neon DB?
Neon is a fully managed serverless PostgreSQL database designed for modern apps. It offers:
- Git-style branching for databases
- Auto-scaling serverless architecture
- Generous free tier
- Smooth integration with Drizzle and other tools
In short: it's PostgreSQL for the cloud-native era.
How Do Drizzle and Neon Work Together?
These two tools are made for each other:
- Neon hosts your cloud-based PostgreSQL database
- Drizzle connects to Neon using a connection string
- You write type-safe queries in Drizzle, and Neon runs them
Example setup:
import { neon } from '@neondatabase/serverless';
import { drizzle } from 'drizzle-orm/neon-http';
const sql = neon(process.env.DATABASE_URL!);
const db = drizzle(sql);
Example query:
await db.select().from(todos).where(eq(todos.userId, 1));
Getting Started
Let's begin by setting up our Node.js project.
Prerequisites
Make sure you have Node.js installed. If not, download it here.
Project Setup
Step 1: Create Project Folder
Create a folder and give it any name (we'll use todo-api-drizzle-neon):
mkdir todo-api-drizzle-neon
cd todo-api-drizzle-neon
Step 2: Initialize the Project
Run:
npm init -y
This will create a package.json file for you.
Step 3: Create the Source Folder
Inside your root folder, create a src folder. This is where your app logic will live.
Then create an index.ts file inside it:
todo-api-drizzle-neon/
└── src/
└── index.ts
Step 4: Install Dependencies
Install the required packages:
npm install express drizzle-kit drizzle-orm typescript @neondatabase/serverless dotenv
npm install --save-dev @types/express
Your package.json should now look like this:
{
"name": "todo-api-drizzle-neon",
"version": "1.0.0",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"dev": "nodemon src/index.ts",
"db:push": "drizzle-kit push",
"db:studio": "drizzle-kit studio",
"db:generate": "drizzle-kit generate",
"db:migrate": "tsx ./src/db/migrate.ts"
},
"dependencies": {
"@neondatabase/serverless": "^0.10.4",
"dotenv": "^16.5.0",
"drizzle-kit": "^0.31.1",
"drizzle-orm": "^0.44.1",
"express": "^5.1.0",
"typescript": "^5.8.3"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/express": "^5.0.2"
}
}
Step 5: Create a tsconfig.json File
Create a tsconfig.json file in your root directory:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"lib": ["es5", "es6"],
"target": "ES2018",
"module": "commonjs",
"moduleResolution": "node",
"rootDir": "./src",
"outDir": "dist",
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true,
"experimentalDecorators": true,
"sourceMap": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"resolveJsonModule": true,
"typeRoots": ["./src/types", "./node_modules/@types"]
},
"include": ["src/**/*.ts"],
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
}
Setting Up the Database
Step 1: Create a Neon Account
- Go to https://neon.tech and sign up for a free account
- Create a new project
- Copy your connection string from the dashboard
Step 2: Set Up Environment Variables
Create a .env file in your project root:
DATABASE_URL="your-neon-connection-string"
PORT=4000
Also, create a .gitignore file:
node_modules
.env
Step 3: Create Database Schema
Create src/db/schema.ts:
import { pgTable, serial, text, boolean } from 'drizzle-orm/pg-core';
export const todos = pgTable('todos', {
id: serial('id').primaryKey(),
task: text('task').notNull(),
completed: boolean('completed').default(false),
});
Step 4: Set Up Database Connection
Create src/db/index.ts:
import dotenv from 'dotenv';
dotenv.config();
import { neon } from '@neondatabase/serverless';
import { drizzle } from 'drizzle-orm/neon-http';
import * as schema from './schema';
const sql = neon(process.env.DATABASE_URL!);
export const db = drizzle(sql, { schema });
Step 5: Configure Drizzle
Create drizzle.config.ts:
import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';
import { defineConfig } from 'drizzle-kit';
dotenv.config();
export default defineConfig({
schema: './src/db/schema.ts',
out: './drizzle',
dialect: 'postgresql',
dbCredentials: {
url: process.env.DATABASE_URL!
},
migrations: {
table: '__drizzle_migration',
schema: 'public'
},
verbose: true,
strict: true
});
Step 6: Push Schema to Database
Run:
npm run db:push
Implementing the Todo API
Now that our database is set up, let's create a RESTful API for managing todos.
Project Structure
src/
├── db/
│ ├── index.ts # Database connection
│ ├── schema.ts # Table definitions
│ └── migrate.ts # Migration script
├── routes/
│ └── todos.ts # Todo API endpoints
└── index.ts # Express app setup
Step 1: Create Express Server
Update src/index.ts:
import express from 'express';
import dotenv from 'dotenv';
import todoRoutes from './routes/todos';
dotenv.config();
const app = express();
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 4000;
// Middleware
app.use(express.json());
// Routes
app.use('/api/todos', todoRoutes);
// Health check endpoint
app.get('/health', (_req, res) => {
res.json({ status: 'ok' });
});
// Centralized error handling middleware
app.use((err: Error, _req: express.Request, res: express.Response, _next: express.NextFunction) => {
console.error(err.stack);
res.status(500).json({
error: 'Something went wrong!'
});
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`🚀 Server running at http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});
Step 2: Implement Todo Routes
Create src/routes/todos.ts:
import { Router, RequestHandler } from 'express';
import { db } from '../db';
import { todos } from '../db/schema';
import { eq } from 'drizzle-orm';
const router = Router();
// Create a new todo
const createTodo: RequestHandler = async (req, res, next) => {
try {
const { task } = req.body;
if (!task || typeof task !== 'string') {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Task is required and must be a string'
});
return;
}
const [newTodo] = await db.insert(todos)
.values({ task })
.returning();
res.status(201).json(newTodo);
} catch (error) {
next(error); // Pass to error handling middleware
}
};
// Get all todos
const getAllTodos: RequestHandler = async (_req, res, next) => {
try {
const allTodos = await db.select().from(todos);
res.json(allTodos);
} catch (error) {
next(error);
}
};
// Get a single todo
const getTodoById: RequestHandler = async (req, res, next) => {
try {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
if (isNaN(id)) {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Invalid todo ID'
});
return;
}
const [todo] = await db.select()
.from(todos)
.where(eq(todos.id, id));
if (!todo) {
res.status(404).json({
error: 'Todo not found'
});
return;
}
res.json(todo);
} catch (error) {
next(error);
}
};
// Update a todo
const updateTodo: RequestHandler = async (req, res, next) => {
try {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
const { task, completed } = req.body;
if (isNaN(id)) {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Invalid todo ID'
});
return;
}
// Validate input
if (task !== undefined && typeof task !== 'string') {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Task must be a string'
});
return;
}
if (completed !== undefined && typeof completed !== 'boolean') {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Completed must be a boolean'
});
return;
}
// Update todo
const [updatedTodo] = await db.update(todos)
.set({
...(task !== undefined && { task }),
...(completed !== undefined && { completed })
})
.where(eq(todos.id, id))
.returning();
if (!updatedTodo) {
res.status(404).json({
error: 'Todo not found'
});
return;
}
res.json(updatedTodo);
} catch (error) {
next(error);
}
};
// Delete a todo
const deleteTodo: RequestHandler = async (req, res, next) => {
try {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
if (isNaN(id)) {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Invalid todo ID'
});
return;
}
await db.delete(todos)
.where(eq(todos.id, id));
res.status(204).send();
} catch (error) {
next(error);
}
};
// Register routes
router.post('/', createTodo);
router.get('/', getAllTodos);
router.get('/:id', getTodoById);
router.patch('/:id', updateTodo);
router.delete('/:id', deleteTodo);
export default router;
Step 3: Test the API
Start the server:
npm run dev
Test the endpoints using curl or Postman:
- Create a todo:
curl -X POST http://localhost:4000/api/todos \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"task": "Learn Drizzle ORM"}'
- Get all todos:
curl http://localhost:4000/api/todos
- Get a specific todo:
curl http://localhost:4000/api/todos/1
- Update a todo:
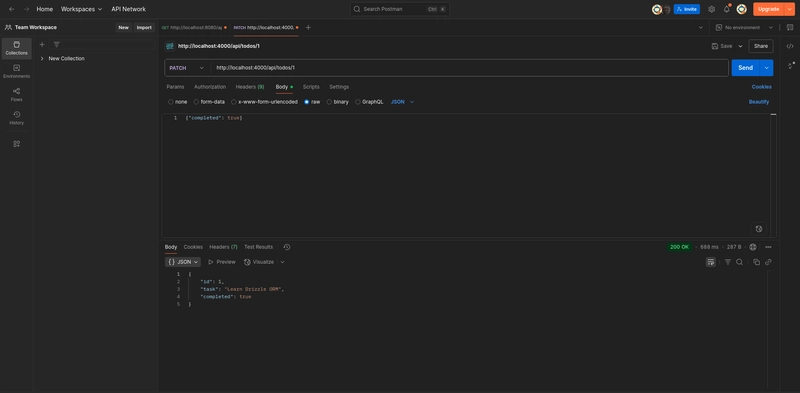
curl -X PATCH http://localhost:4000/api/todos/1 \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"completed": true}'
- Delete a todo:
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:4000/api/todos/1
Conclusion
In this guide, we've built a type-safe Todo API using:
- TypeScript for type safety
- Drizzle ORM for database operations
- Neon for serverless PostgreSQL
- Express for the API server
The result is a modern, scalable, and maintainable backend that's ready for production use. With TypeScript and Drizzle, we gain excellent type safety and developer experience. Neon gives us a cloud-native database that scales effortlessly.
If you found this article helpful, don’t forget to leave a like and drop a comment it really helps!
🔗 Stay connected:
Project Repository: View it on GitHub
Thanks for reading, and happy coding! 🚀








Nicee!!
I use Neon DB often, it’s a cool one! Will check out Drizzle