Today marks the end of my #30DaysLinuxChallenge journey!
I’m closing it out with a practical, security-focused project: building and executing a Linux server hardening and auditing checklist on Red Hat Linux.
This is a perfect combination of RHCSA exam skills + real-world system administration practices.
🎯 Objective
- Apply basic hardening policies
- Configure auditing with
auditd - Create a personal security validation checklist
- Monitor and analyze system logs
📚 RHCSA Skills Covered
✔ User and password security
✔ SELinux & firewall validation
✔ Service management
✔ Log auditing with journalctl and auditd
✔ Shell scripting for checks
📝 Server Hardening Checklist
✅ 1. Set Strong Password Policy
sudo nano /etc/login.defs
Adjust values:
PASS_MAX_DAYS 90
PASS_MIN_DAYS 7
PASS_WARN_AGE 7
✅ 2. Disable Unnecessary Services
sudo systemctl disable --now cups
sudo systemctl disable --now bluetooth
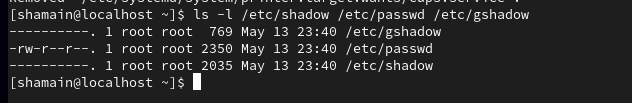
✅ 3. Set File Permissions on Critical Files
ls -l /etc/shadow /etc/passwd /etc/gshadow
✅ 4. Verify SELinux is Enforcing
sestatus
Expected:
SELinux status: enabled
Current mode: enforcing
✅ 5. Harden SSH Configuration
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Recommended settings:
PermitRootLogin no
PasswordAuthentication no
MaxAuthTries 3
Restart SSH:
sudo systemctl restart sshd
✅ 6. Enable and Check Firewall Rules
sudo firewall-cmd --state
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all
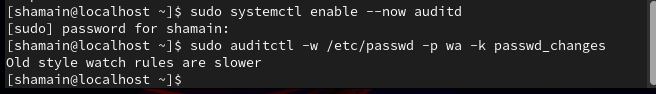
✅ 7. Set Up Auditing with auditd
sudo dnf install -y audit
sudo systemctl enable --now auditd
Monitor file access:
sudo auditctl -w /etc/passwd -p wa -k passwd_changes
View audit logs:
sudo ausearch -k passwd_changes
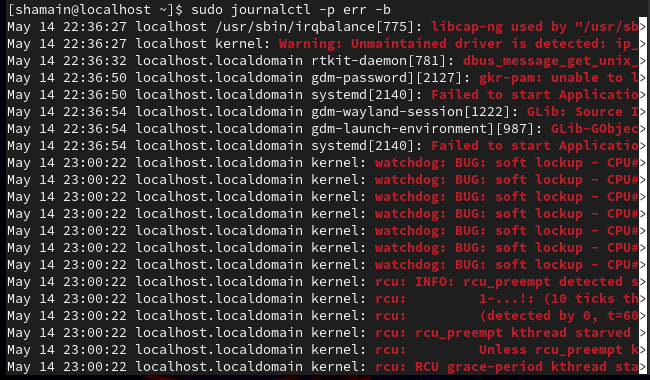
✅ 8. Monitor Logs
sudo journalctl -p err -b
sudo tail -f /var/log/secure
✅ 9. Create a Custom Validation Script (Bonus)
nano ~/server_check.sh
Example:
!/bin/bash
echo "Checking SELinux status:"
sestatus
echo "Checking firewall state:"
firewall-cmd --state
echo "Checking SSH root login setting:"
grep PermitRootLogin /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Make executable:
chmod +x ~/server_check.sh
Run:
./server_check.sh
✅ Recap
| Task | Tool/Command |
|---|---|
| Password policy | /etc/login.defs |
| Disable services | systemctl disable --now |
| Check file permissions | ls -l |
| Check SELinux | sestatus |
| Harden SSH | sshd_config |
| Enable firewall | firewall-cmd |
| Configure auditing |
auditctl, ausearch
|
| Analyze logs |
journalctl, tail
|
🎉 Why This Matters
This project combined almost every core RHCSA skill:
- Service & user management
- SELinux & firewall security
- System auditing
- Scripting and automation
In the real world, this is the starting point of any secure Red Hat deployment.